Hey there! This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate, I earn a teensy commission from qualifying purchases when you buy through these links (at no additional cost to you). For more info, please check the full disclaimer.
Ovarian cancer usually occurs in women over the age of 50 years and can affect one or both ovaries. It is the 7th most common type of cancer in women. Hence, it’s important to know about the causes of ovarian cancer and how to prevent this disease.
No single cause of ovarian cancer has been identified yet, but several factors can lead to its prognosis. In this blog, we’ll discuss some of the common and rare causes of ovarian cancer and things you can do to prevent the onset of this disease.
What is Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer is the uncontrolled proliferation of cancerous cells present in the lining of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or uterine walls. As these cells multiply rapidly, they form large clusters called tumors that can potentially migrate to other organs.
Four different types of ovarian cancer are mentioned below:
- Epithelial ovarian cancer
- Borderline ovarian tumors
- Germ cell ovarian tumors
- Sex cord stromal tumors
Various factors influence the causes of ovarian cancer, such as genetics, environment, and lifestyle choices. According to a study, ovarian cancer has less than 45% of survival rate five years after diagnosis and is the eighth leading cause of death in women.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that 10 in every 100,000 women in 2019 were diagnosed with ovarian cancer.
Hence, knowing what causes ovarian cancer and how to stay safe from this dangerous disease is critical.
What are the Signs of Ovarian Cancer?
The early stages of ovarian cancer have mild symptoms, resembling a common stomach bug or food poisoning, making it difficult to diagnose. As a result, for a long time, ovarian cancer was referred to as ‘the silent killer.’
According to a study conducted in 2011, the three most common combinations of symptoms are:
- Abdominal pain
- Abdominal bloating
- Increased abdominal size
Some other symptoms of ovarian cancer commonly reported by patients are:
- Increased satiety levels
- Unintentional weight change
- Pelvic pain
- Frequent and painful urination
Read More: 11 Subtle Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
What are the Main Causes of Ovarian Cancer?
Despite the continued advancement of medicine, scientists are yet to determine the exact causes of ovarian cancer. So far, researchers have discovered a few factors that increase women’s chances of ovarian cancer.
Ovarian cancer is primarily caused by alterations in the genetic makeup known as DNA. It entices the cells of the lining of ovaries or fallopian tubes to replicate rapidly, forming clusters of cells called tumors.
These tumors then detach from their primary organ and metastasize to the surrounding tissues.
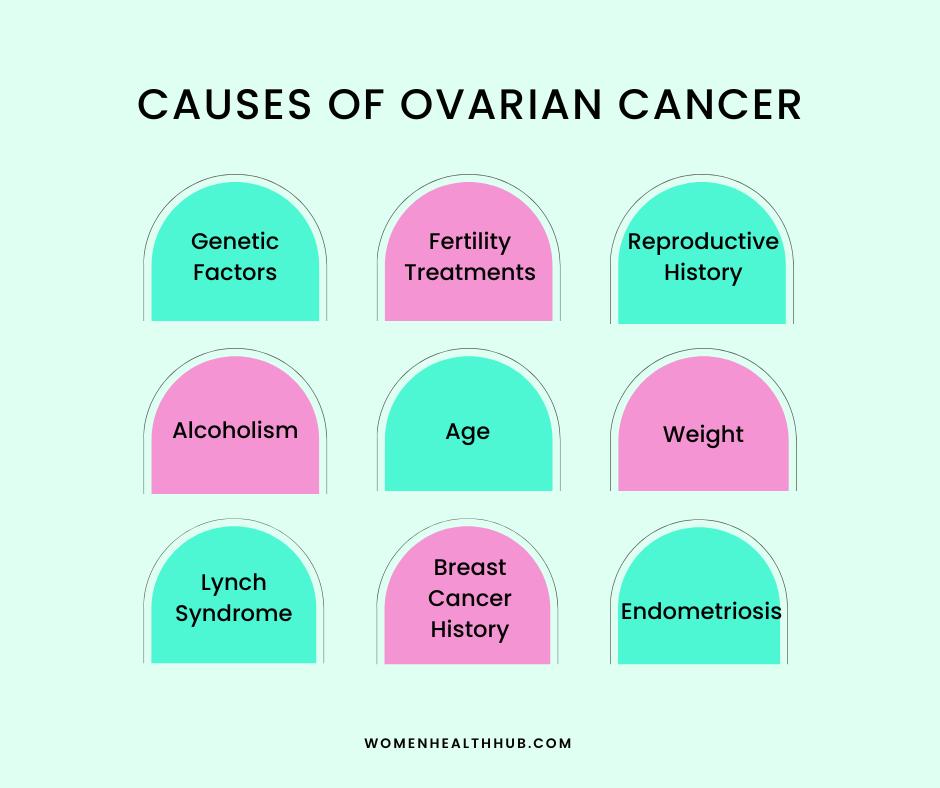
Some of the common causes of ovarian cancer are described below:
1. Ethnicity
The risk of cancer differs among different ethnicities, with certain types being more prevalent in some racial groups than others.
In 2018, ovarian cancer statistics showed that white Americans are more prone to ovarian cancer. In contrast, the prevalence of ovarian cancer was lowest in African Americans and Asian/Pacific Islanders.
2. Age
The risk of ovarian cancer increases gradually with age. Post-menopausal women are more likely to develop ovarian cancer than women younger than forty-five years.
A study has estimated that about 48% of all ovarian cancer cases occur in women older than 65.
Read More: 15 Must-Follow Tips to Prevent Cancer
3. Weight
Higher than average body mass index (BMI) is also one of the most significant causes of ovarian cancer, especially in postmenopausal women.
Research published in Cancer Reports in 2022 showed that the risk of ovarian cancer was more significant in obese women than in overweight women.
Fat cells are vital for producing hormones, including estrogen and progesterone. The greater amount of fat in the body leads to higher circulating estrogen levels, which stimulates the ovarian cells to replicate, increasing the risk of cancer.
Read More: 15 Nutritious Foods to Boost Estrogen Naturally
4. Hereditary Factors
Ovarian cancer has a strong genetic link and tends to run in the family. BRCA1 and BRCA2 are tumor suppressor genes that protect, review, and repair DNA during replication. The mutations
causes unchecked multiplication of cells leading to enhanced susceptibility to both ovarian and breast cancer.
According to Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), about 10% of the total cases of ovarian cancer per year result from genetic mutations in the BRCA gene inherited within a family.
Screening tests are available to determine any genetic mutations and start treatment for hereditary causes of ovarian cancer at an early stage.
5. Family History
Having an immediate family member like a grandmother, mother, or sister with ovarian or breast cancer also increases your chances of developing this disease by three times. The greater the number of relatives with ovarian cancer, the greater the probability for you to develop the symptoms.
6. Lynch Syndrome
Lynch syndrome, known as hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC), is caused by inherited gene mutations that hinder the body’s ability to fix any mistakes during DNA replication.
The occurrence of Lynch syndrome increases the risk of many different types of cancer, including ovarian cancer. According to a study, about 10-15% of all hereditary ovarian cancer is caused by Lynch syndrome.

7. History of Breast Cancer
If you have had breast cancer, it may also become one of the causes of ovarian cancer.
Your likelihood of developing ovarian cancer increases as the causal factors of breast cancer are similar to that of ovarian cancer. The start of menses, fertility treatments, and mutations in BRCA genes increases ovarian and breast cancer onset.
The possibility of ovarian cancer increases exponentially in women diagnosed with breast cancer at a younger age.
Read More: 9 Alarming Symptoms of Breast Cancer
8. Fertility Treatments
Women undergoing treatments for infertility are also at a higher risk of developing ovarian cancer. Fertility treatments disturb the levels of estrogen hormones and induce ovulation, increasing the risk of cyst production.
According to a study conducted in 2018, women who conceive and deliver successfully may lower their chances of ovarian cancer compared to women who cannot conceive with fertility drugs.
Thus, discussing the associated risks with your doctor before starting fertility treatments is highly recommended.
Read More: 15 Best Fertility Herbal Teas to Get Pregnant Naturally
9. Reproductive History
Previous reproductive diseases or disorders are also important causes of ovarian cancer.
According to research, full-term pregnancies act as a protective factor against ovarian cancer as it halts the process of ovulation. Similarly, the greater the number of full-term pregnancies, the lower the risk.
According to the American Cancer Society, having first pregnancy after the age of thirty-five or never carrying a pregnancy to term also boosts the chances of ovarian cancer.
10. Age of Menarche and Menopause
Girls who have periods before 12 years are said to be at a higher risk of ovarian cancer. Late-onset menopause after 55 years of age is also associated with ovarian cancer.
Early menses and late menopause mean a constant production of sex hormones and ovulation for an extended period of time, both of which are attributed to the onset of ovarian cancer.
11. Hormonal Replacement Therapy (HRT)
Hormonal replacement therapy has both benefits and risks for women going through menopause. It can effectively alleviate the symptoms associated with menopause but potentially increase the risk of onset of ovarian cancer.
Hormonal replacement therapy uses exogenous estrogen to combat the severity of menopausal symptoms. The use of replacement therapy elevates the levels of estrogen hormone, making these women susceptible to ovarian cancer.
12. Smoking
Scientists are still determining whether or not smoking is among the causes of ovarian cancer.
Per a study conducted in 2013, smoking increases the risk of a mucinous ovarian tumor but cannot be associated with invasive ovarian cancer.
13. Alcohol
Alcohol consumption increases the circulating levels of estrogen hormones in the body. In 2015, a study determined that women who drank large quantities of alcohol had a higher risk of developing ovarian cancer than non-drinkers.
14. Endometriosis
Experts are still exploring how endometriosis could be one of the causes of ovarian cancer. Endometriosis leads to higher concentrations of estrogen levels, inducing the growth of tumors. In endometriosis, the menstrual blood flow can displace the endometrial cells, which can become invasive over time.

Although all women with endometriosis do not develop ovarian cancer, a study published in 2017 showed that endometriosis increases the chances of developing ovarian cancer by 1.7 times.
How Can You Prevent the Risk of Ovarian Cancer?
As physicians cannot pinpoint the exact cause of ovarian cancer, no specific method can reduce the overall risk of ovarian cancer. Women with a family history of ovarian cancer should opt for testing and counseling to assess their risk and preventative approaches.
While there are no guaranteed methods for hindering ovarian cancer, adopting healthy habits and proactively monitoring health can help reduce the risks and improve overall health.
A group of practices that can reduce the causes of ovarian cancer are discussed below.
- Staying Within the Healthy Range of BMI
Body Mass Index (BMI) determines the ideal body weight of a person in relation to their height. Maintaining a BMI between 18.5-24.9kg/m² ensures better physical health with a low risk of various types of cancer.
- Oral Contraception
Most women use oral contraception as birth control pills to subdue the severe symptoms associated with menstruation.
According to National Cancer Institute, long-term use of contraception also reduces the risk of ovarian cancer by 30-50% in women compared to those who have never taken birth control pills.
- Screening Tests
Another way to counter the causes of ovarian cancer is through periodic health screening tests.
Genetic testing is available that determines the presence of mutations in the BRCA genes. CA-125 blood tests, transvaginal ultrasounds, and pelvic exams are all part of screening and diagnosis of ovarian cancer.

Similarly, due to the close link of ovarian cancer with breast cancer, a mammogram is also available to detect the presence of tumors in breast tissues.
Read More: How to Prepare for a Mammogram
- Breastfeeding
Getting pregnant and completing a full-term suppresses the potential progression of ovarian cancer. Similarly, according to studies, women who breastfeed for a minimum of a year are less likely to develop ovarian cancer after menopause.
- Discuss with Your Doctor
If you are at high risk due to any of the causes of ovarian cancer mentioned above, consult your primary physician. They will recommend screening tests and counseling sessions that can help in the early detection and monitoring of your symptoms.
The Bottomline
Ovarian cancer is a complex disease with no particular cause, which makes it difficult to detect in the early stages.
Various factors lead to causes of ovarian cancer, stimulating the proliferation of cells, like race, age, individual and family medical history, reproductive choices, and many more.
Regular checkups with healthcare providers and taking proactive measures for detecting, monitoring, and treating ovarian cancer can improve the onset of those affected.
References:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3818570/
- https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/ovarian/basic_info/prevention.htm
- https://gis.cdc.gov/Cancer/USCS/#/AtAGlance/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3806278/
- https://obgyn.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/1471-0528.14831








