Hey there! This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate, I earn a teensy commission from qualifying purchases when you buy through these links (at no additional cost to you). For more info, please check the full disclaimer.
Did you know that diabetes in women is among the top ten causes of death in the US?
Scary!
Right now, more than 200 million women are diabetic, and numbers are expected to reach 300+ million by 2040.
Sadly, most diabetic cases are either undiagnosed or untreated. This leads to many health complications and may even reduce your lifespan!
Once you understand the causes and signs of high blood sugar and how to manage it, you can create a proper management plan and avoid further risking your health.
Dr. Scott Soleimanpour, who himself has type 1 diabetes, emphasizes educating yourself about the disease.
“It’s important for diabetics to empower themselves. You can’t be a backseat driver with your diabetes.”
Michigan Medicine – University of Michigan
In this blog, I will explain everything women must know about chronic high blood sugar, including some ways to manage diabetes naturally.
So without further ado, let’s get started.
What is Diabetes in Women?
Diabetes, or diabetes mellitus, is a disease caused by high blood sugar (blood glucose) levels.
Diabetics either don’t produce insulin or are resistant to its function. Insulin is a pancreatic hormone responsible for absorbing glucose from your bloodstream as the body’s main energy source.
Types of Diabetes in Women
Diabetes is categorized into four main types:
Type 1 diabetes:
Type 1 diabetes affects the production of insulin in the pancreas. It is an autoimmune disease that causes the body’s own immune system to attack insulin-producing cells.
Type 2 diabetes:
In type 2 diabetes, you are unable to process the glucose present in the bloodstream because of insulin resistance, which spikes the sugar levels in your body.
Prediabetes:
Prediabetes is not an illness but determines whether you’re at risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future.
Gestational diabetes:
Some pregnant women’s bloodstream contains a high amount of excess blood sugar. This condition is called gestational diabetes. All extra glucose is then absorbed by the baby, causing overgrowth at delivery time. Gestational diabetes can cause either hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia based on glucose levels.
Read More: 7 Signs of Gestational Diabetes
Diabetes in Women: Causes & Symptoms
If you want to catch diabetes in the early stages, you must know what happens if you have high blood sugar.
Even though diabetes mellitus has many types, luckily, all show similar signs and causes.
Let’s take a look at a few reasons and common symptoms of diabetes among women.
Causes of diabetes in women
Type 1 & Type 2 Diabetes
- Family history/ethnicity
- Age
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Lack of physical activity
- Alcoholism
- Low weight at birth time
- Untreated Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
- Low fiber/high-fat diet
- Vitamins deficiency
Gestational Diabetes
- Family history/ethnicity
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOs)
- Exposure to toxins during pregnancy
- Age 25+ years old
- Previously delivered an overweight infant
- High amniotic fluid in the body
Prediabetes
- History of gestational diabetes
- Family history/ethnicity
- Obesity
- Hormonal imbalance
- Stress
- High blood glucose levels
- Previously delivered an overweight infant
Symptoms of diabetes in women
- High blood pressure
- Swollen feet
- Fatty liver
- Tiredness
- Increased appetite
- Weight loss
- Blurred vision
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Skin infections/dark spots
- Vaginal itching
- High blood sugar levels
Read More: 14 Early Warning Signs of Diabetes in Women
How Common is Diabetes Among Women?
Although the rate of new diabetes diagnosis has dropped from 1.7 million in 2009 to 1.3 million in 2017, the number of diabetic women cases is still alarming!
According to CDC, the number of annual female diabetic patients has risen by 4% since 1980.
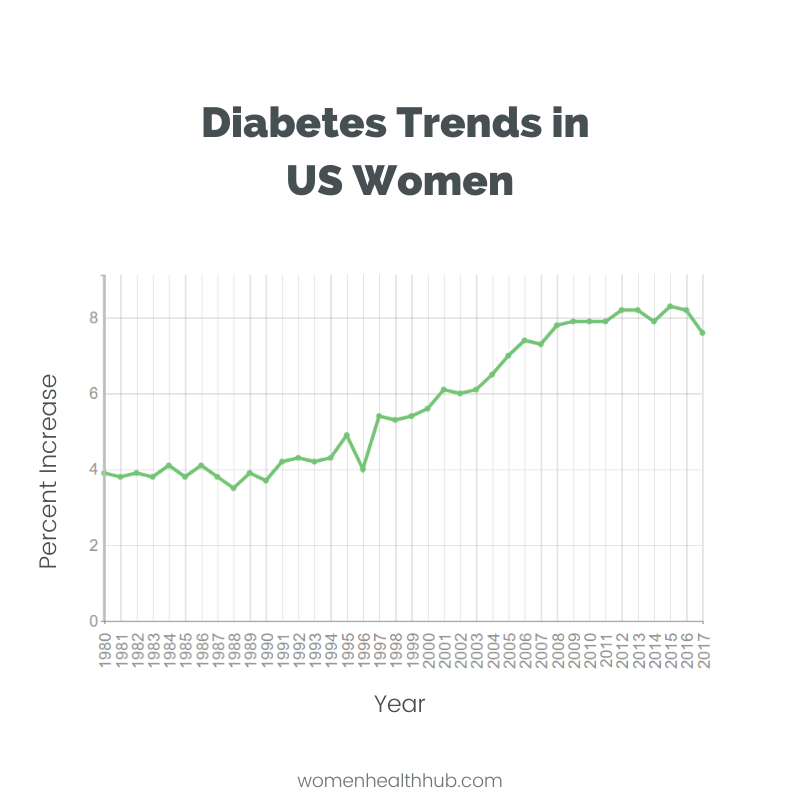
Another research shows a dramatic escalation in women’s diabetes between 2010 and 2019 – approximately 1 million every year!
Considering the big picture, more than 6 million women in the US currently have been diagnosed with diabetes. Imagine the numbers if we add undiagnosed cases to the count too!
Because most women have limited awareness about self-management of diabetes, it has been difficult to control the numbers.
Understanding diabetes symptoms and causes can help you identify the disease and start a diabetes management plan right away.
Now that we have established this illness’s cause, symptoms, and impact, let’s see what happens if diabetic symptoms are not managed on time.
Health Problems Caused by Untreated Diabetes in Women
Studies confirm that if you neglect diabetes mellitus symptoms, you may experience various health complications and long-term diseases.
Here’s a brief overview of some health problems caused by diabetes.

1. Diabetic Kidney Disease
A 2016 research in Missouri Medical reported diabetic kidney disease as the leading cause of kidney failure in the US.
Previously, a 2012 study in the American Journal of Nephrology established that this disease affects women aged 60+ years.
Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes injure kidney blood vessels which can impair their functioning. As a result, salt in the body increases, leading to high blood pressure and obesity.
Also, many diabetic women suffer from bladder infections due to damaged nerves, rendering them unable to urinate when needed.
2. Heart Diseases
Women who have type 1 or type 2 diabetes, respectively, have 45% and 9% more risk of heart failure than men, per a published article in Diabetologia.
Additionally, diabetic women have a 27% higher chance of getting a stroke compared to men.
Consistently high blood sugar levels ruin your cardiovascular health. If you fail to manage diabetes, it can develop cholesterol or high blood pressure, leading to symptoms of a heart attack.
Read More: 12 Ways to Prevent Heart Attack Symptoms in Your 40s
3. Birth Defects
Have you noticed a sudden increase in birth defects within the last few decades?
After compiling 15 years of data into a study, scientists revealed that pregestational diabetes is among the top causes of birth disabilities and malformations.
To save your little one from future complications, do test your blood sugar if you notice any diabetic symptoms before or during pregnancy.
Read More: 11 Tips to Prevent Birth Injuries
4. Vision Problems
Even though diabetic retinopathy or blindness, is not usual among women, it’s not insignificant enough to be ruled out of this list.
Most diabetic vision problems occur among women aged 50 to 60 years.
If you’ve had diabetes for a decade, there may be a chance of developing some vision impairment, such as blurriness. But if you leave diabetes unmanaged for several years, it can eventually cause blindness.
5. Organ Infections
Diabetics suffer frequent internal infections as high blood sugar destroys your body’s immunity.
For example, diabetic women usually develop kidney infections causing gas to accumulate in cells.
Another infection increases bacteria in the urine. Sometimes, the bladder lining also gets affected by abnormal gas in cells.
In short, untreated diabetes makes your body vulnerable to infections which can get harder to treat as you age. Not to mention the financial burden it can lead to!
6. Oral Diseases
A 2018 Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences article focused on the relationship between diabetes and dental diseases.
Results revealed more than 90% of diabetic patients normally have some oral disease. Ranging from tooth decay, cavities, and salivary or taste problems, to inflammation and slow healing of oral injuries, the scientists uncovered many diabetes-related oral health complications.
Another 2013 study in the Journal of Applied Oral Science linked women with gestational diabetes to the risk of losing teeth and inflamed gums.
If you’ve had diabetes for years, it’s about time you paid a visit to a dentist to save your beautiful smile!
7. Foot Diseases
Elderly diabetic women aged 80+ years may develop foot diseases as a result of calluses and claw toes.
However, diabetic foot is more common in men because women take better care of their feet!
8. Sexual Dysfunction
Women with type 2 diabetes often have problems in bed. Vaginal dryness, anxiety, difficulty in orgasms, decreased sexual drive, and difficulty in getting aroused affects many diabetic females.
Sexual dysfunction may be caused by hormonal imbalance or age’s impact on libido. In a few cases, depression also reduces sexual drive.
Read More: 10 Best Sex Positions for Women to Increase Pleasure
9. Skin Diseases
If diabetes mellitus is not managed properly, it might wreck your skin. Women aged between 40 to 60 years may experience skin lesions. They are harmless but, in most cases, turn into painful ulcers.
Fungal infections in diabetic women, particularly in the vagina, are also reported in some studies.
Controlling blood sugar can help you keep diabetic skin infections at bay.
10. Deafness
A 2019 study in Diabetologia confirmed that women who’ve had type 2 diabetes for over a decade are prone to hearing loss. Sometimes, it may result in deafness.
If you manage type 2 diabetes in the early stages, you can avoid this disease.
11. Bone Diseases
Postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes also develop bone diseases. After you hit the 40s, the bone density decreases because of high blood glucose, resulting in hip or wrist fractures.
In some cases, bone marrow fat increases in the vertebrae/spine. Osteoporosis is another bone issue targeting women with consistently high blood sugar levels.
one degenerative diseases are usually caused by calcium and vitamin deficiency. They are difficult to reverse unless you start a separate bone health management plan.
Read More: 12 Ways to Prevent Osteoporotic Fractures
12. Cancers
Diabetic symptoms grow into cancer in the worst cases. A study showed an increased risk of gastric, colorectal, breast, and kidney cancers among females compared to males with high blood glucose.
A researcher at Imperial School of Public Health, Dr. Jonathan Pearson-Stuttard, confirmed the link between diabetes and cancer.
“Our study shows that diabetes, either on its own or combined with being overweight, is responsible for hundreds of thousands of cancer cases each year across the world.”
Dr. Jonathan Pearson-Stuttard, Imperial School of Public Health
Unmanaged diabetes causes harm to your organs by mutating the cells and eventually leads to cancer. Sometimes, increased insulin levels also turn into cancers.
However, if you follow strict diets and make sufficient changes in your lifestyle, you can successfully reduce the risk of cancer in the long run.
Read More: 15 Tips to Prevent Cancer Risk
13. Early Death
Postmenopausal women with diabetes mellitus and related conditions are likely to die earlier than those who are not diabetic. The most common reason for early death among diabetic women is heart attacks.
Research shows that diabetic women can die within a year after having a heart attack. It’s because blood glucose affects your immunity, leads to obesity, and weakens your heart. So the body has limited protection against diseases.
Luckily, it’s not all bad news!
After hitting 50, you can live up to 4 years or more if you are physically active. In most cases, diabetes can even be reversed by following vigorous exercise routines.
How to Control Diabetes Symptoms?
Primarily, you must consult a doctor or specialist right away as soon as you experience early signs of diabetes. Modern medicine regulates insulin deficiency and blood sugar levels.
But at the same time, it’s necessary to have a self-care plan for diabetes management.
Let’s get real for a bit: there is no absolute cure for diabetes. And at one point, you might have the urge to throw out the medicines.
If you want to live with diabetes without relying completely on medications, a comprehensive self-care plan can be your savior.
Mastering diabetes self-management can have the following benefits for you:
- Boosts the effect of modern medicinal treatment
- Reverses symptoms to the point that you won’t need medicines
- Enables you to be more physically active
- Gives you the confidence to tackle and control the symptoms
- Helps you cope with future blood sugar complications
The simplest way to cure diabetes mellitus symptoms yourself is through lifestyle changes and by monitoring what you eat.
Let’s see how it works.
Tip #1: Manage diabetes with proper diet

If you’re diabetic, you are advised to cut down on sugar and carb-filled foods to keep your blood glucose levels and weight in check.
Numerous researches have shown that women are more prone to getting obese than men. That’s because men are more physically active, making it easier for their bodies to process fat.
Benefits:
Numerous proven diet plans show good results for diabetic patients. Here are some ways it can benefit your overall well-being:
- Lowers risk of heart diseases
- Optimizes blood glucose
- Prevents cancer development
- Promotes the consumption of nutritious foods
Your goal:
When it comes to managing diabetes symptoms with diet, you have two main outcome goals:
- Managing weight
- Balancing blood sugar level
Below, I’m sharing a few popular self-diet management methods for diabetics:
Portion Control:
Giving up on your favorite foods can be super difficult. I mean, we are humans after all!
Perhaps the best way to be mindful of what you eat is by adopting the portion control approach.
You don’t have to make sacrifices in terms of WHAT you eat but rather check HOW MUCH you’re eating.
In other words, you can eat almost anything as long as you control its amount.
It’s important to figure out what portion size is suitable for your body type, though. Consult with a dietician to understand what works for you.
Ketogenic Diet:
Keto is a technique that relies on fat as the core source of energy instead of carbs.
Normally, carbs provide us body fuel. But in keto, you avoid carbs altogether. You can only consume high-fat foods that are later used up as energy. Afterward, natural body fat is metabolized instead.
Ketogenic diet plan reduces the risk of obesity—one of the core symptoms that worsen diabetes among women. Particularly, type 1 diabetic women swear by its effectiveness.
Macrobiotic Diet:
Macrobiotic diet originated from Zen Buddhism, involving strict dietary habits with an aim to balance your physical and mental wellness.
Primarily, this diet is free of meat consumption, spices, some fruits, juices, dairy products, eggs, and even select vegetables. In fact, it’s almost like veganism and you’re required to eat organically produced foods.
The macrobiotic diet demands a lot of effort for cooking. However, diabetics can benefit from its no-fat-no-sugar principles and consume nutritious foods every day.
Tip #2: Manage diabetes by changing lifestyle
Another effective self-management trick to treat diabetes is by making a few lifestyle changes.
Your lifestyle encompasses multiple factors, such as diet, exercise, daily routines, leisure activities, etc.
Benefits
These are the long-term benefits of adopting a healthy lifestyle to treat diabetes:
- Improves physical and mental wellbeing
- Reduces the risk of diabetes-related diseases
- Helps save money that is otherwise spent on medicines
- Enables you to accept the disease and adjust life accordingly
Your goal
Again, your aim here should be to ditch every practice that triggers increased blood sugar.
Below are some ways you can adjust your lifestyle to manage diabetes.
Exercises:
Physical activity is helpful in removing extra fat from your body and improves blood sugar levels.
Even a brief 30 minutes workout balances glucose to the optimal amount, as reported by a 2016 research published in Diabetes Care.
Don’t worry! You can always start with light exercises and work your way up to intense ones.
Also, if you are pregnant and diagnosed with gestational diabetes, mild exercise routines can keep you safe from blood sugar.
Sleep:
Sleeping for more than 9 hours every night puts you at risk of developing diabetes.
So try snoozing for no more than 8 hours and stick to a fixed schedule to wake up and fall asleep at the same time.
Alternative Treatments for Diabetes
No doubt, modern medicinal treatments are necessary to maintain optimal blood sugar levels.
However, complementary treatments also balance using natural techniques and work side-by-side with contemporary treatments.
According to a 2010 study conducted by two medical specialists, Gurjeet Birdee and Gloria Yeh, over 30% of people in the US use some type of complementary therapy to treat symptoms of diabetes mellitus.
Another study revealed that natural health products used for diabetes treatment show amazing results.
But be careful before starting any alternative treatment for high blood sugar — without consulting a specialist first, it may pose negative effects on health.
Popular alternative/complementary diabetes treatments are as follows:
- Ayurveda
- Tai Chi
- Acupuncture
- Herbal and dietary supplements
- Feng Shui
- Naturopathy
- Qigong
- Yoga
- Chinese medicine
- Physical therapies
The Bottomline
Understanding the disease is the first step in your health journey self-care plan.
Now you have an idea how diabetes can affect you in the long run so you can monitor your health in a better way.
It’s completely understandable if you feel overwhelmed by having to manage diabetes symptoms on your own. But trust me, if you take it one step at a time, you can do it.










2 comments
Diabetes is truly a scary disease. So many things can go wrong when your blood sugars aren’t controlled. I have some good friends who are diabetic. One lost her leg to the disease. I was prediabetic before I started a healthier life. I didn’t know I was that close to diabetes until I developed breast cancer. Both those diseases can sneak up on you. I was able to turn my life around with healthy eating and running. Thank you for such a thorough discussion on diabetes. This post is very helpful.
Thank you so much, Patricia. Diabetes really is a scary disease but it’s never too late to control it. Glad you found this article informative. 🙂