Hey there! This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate, I earn a teensy commission from qualifying purchases when you buy through these links (at no additional cost to you). For more info, please check the full disclaimer.
Ovarian cancer is notoriously hard to detect, especially in the early stages. Several tests are recommended for ovarian cancer diagnosis, each offering a different insight into the disease. Scientists are currently working hard to help accurately detect ovarian cancer.
While a mammogram is recommended for the detection of breast cancer and a pap smear for cervical cancer in women, there is still no gold standard tool for detecting ovarian cancer.
In this blog, we will discuss the most common tests for ovarian cancer diagnosis that your doctor may suggest. Plus, you’ll learn about the pros and cons and techniques of these diagnostic procedures.
What is Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer occurs when the cells lining the walls of the ovaries begin to replicate rapidly in an uncontrolled manner. This unchecked proliferation forms a mass of tumors that continue to grow and multiply in size. Ovarian cancer can develop in different parts of the ovaries, ultimately traveling to the surrounding organs of the body.
Various genetic and environmental factors cause ovarian cancer in women. Post-menopausal and overweight women are at higher risk of ovarian cancer than younger women. Similarly, ovarian cancer is strongly associated with genes and tends to run in families.
What are the Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer?
The early stages of ovarian cancer have mild symptoms that usually resemble a stomach bug.
Hence, the ovarian cancer diagnosis may be challenging, earning it the name ‘silent killer.’
Understanding and recognizing the warning signs of this silent disease is essential for timely medical intervention. Some common symptoms of ovarian cancer in women are:
- Bloating
- Early satiety
- Abdominal pain
- Changes in bowel habits
- Heightened fatigue
Read More: 11 Alarming Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
When is Ovarian Cancer Screening Done?
Due to the lack of awareness and poor screening strategies, only 25% of women are diagnosed with ovarian cancer in the early stages.
A late diagnosis of ovarian cancer leads to aggressive treatment plans and a higher risk of morbidity. According to a study, 70-90% of cases of ovarian cancer detected in early stages are curable with adequate treatment.
In the absence of symptoms, women with an average risk of ovarian cancer are not recommended any screening tests. The precautionary steps for these women include educating them about ovarian cancer and providing information on ways to identify the warning signs.
Usually, doctors recommend a pelvic exam to study the size of ovaries or blood tests to determine the presence of cancer antigens.
However, postmenopausal women or those with a family history of ovarian cancer are suggested regular screening scans. The scans recommended for ovarian cancer diagnosis are based on the presence and severity of symptoms, as well as the patient’s personal medical history.
What Tests are Recommended for Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis?
Treatment of ovarian cancer depends on the time of ovarian cancer detection.
According to Ovarian Cancer Research Alliance (OCRA), 89% of women survive for five years if diagnosed with Stage Ⅰ, but the survival rate decreases to 20% at Stage Ⅳ diagnosis.
The lack of specific symptoms, along with the absence of specialized diagnostic tools, presents a challenge in diagnosing the disease accurately.
Let’s discuss the screening tests that are usually employed for ovarian cancer diagnosis:
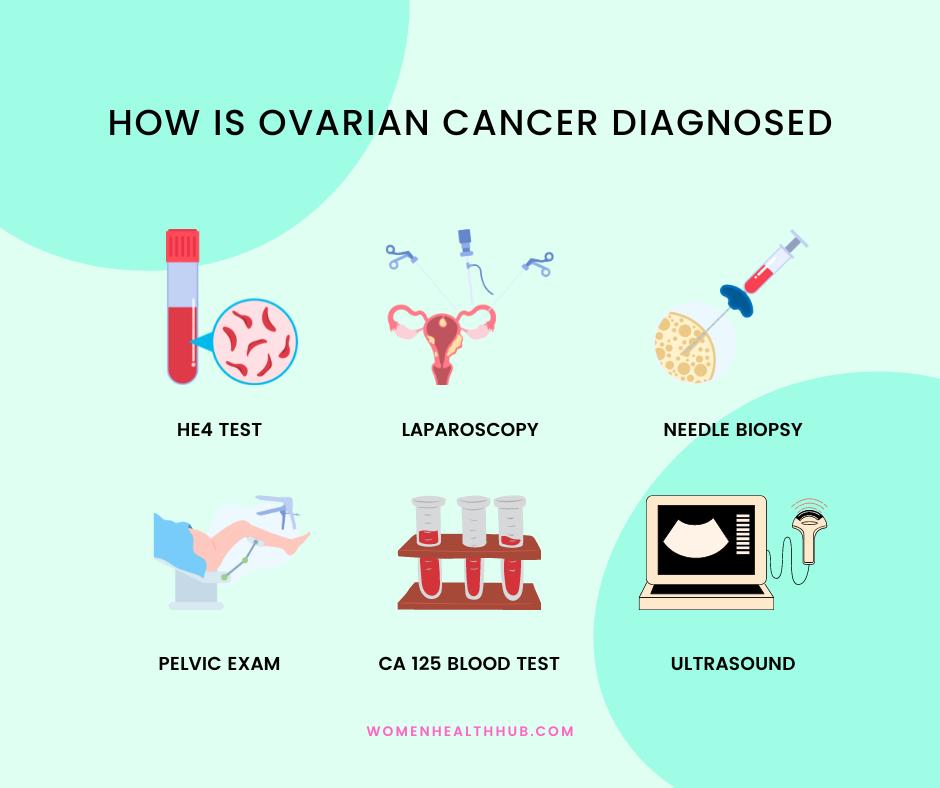
1. CA-125 Blood Test
This test measures the presence of a protein called cancer antigen (CA) in the blood for ovarian cancer detection. CA-125 antigen is used as a biomarker for ovarian cancer as it is produced on the surface of cancerous cells.
CA-125 test is a promising tumor marker, mainly when used in combination with other diagnostic methods. It is non-invasive, so it can be performed regularly and is efficient in monitoring cancer prognosis.
Many women with ovarian cancer diagnosis have high levels of CA-125 antigen in their blood. However, the abnormal levels of this protein are also attributed to certain non-cancerous diseases like endometriosis or uterine fibroids.
According to a study, 7% of non-cancerous women had elevated levels of CA-125 antigen.
In addition, it is also not an accurate determinant for ovarian cancer remission as small numbers of cancerous cells usually fail to raise the CA-125 levels.
Read More: 9 Scary Symptoms of Breast Cancer
2. HE4 Test
HE4 is a protein in the lungs that forms the linings of ovaries. Elevated levels of HE4 are observed in most women with ovarian cancer. This protein is produced in larger quantities in cancerous ovarian cells and is used as an efficient biomarker for ovarian cancer diagnosis.
Due to its efficiency, this is considered a more accurate and reliable method for ovarian cancer detection than the CA-125 blood test. Plus, the HE4 test helps monitor patients with recurring or aggressive forms of this disease.
3. Pelvic Exam
Pelvic examination is the visual and physical assessment of the reproductive organs of women. Pelvic exams are usually done by gynecologists as a part of routine check-ups in women with a higher risk of gynecologic cancers.
The physician will enter two sanitized, gloved fingers into the vagina and place the other hand on the abdomen to gently press down. The doctor studies the size and shape of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus. If the examination reveals anomalies in these organs, further tests are recommended for ovarian cancer detection.
Pelvic exams are rarely accurate on their own, especially in the preliminary stages of ovarian cancer. Only 1% of these exams lead to correct ovarian cancer diagnosis.
Also, these exams fail to differentiate aggressive cancer from benign tumors and need other tests to define the nature of the outgrowth.
Pelvic exams have proven to be quite efficient in diagnosing and monitoring recurring asymptomatic ovarian cancers. Besides ovarian cancer diagnosis, this exam can detect inflammation of the pelvic area, bacterial vaginosis, or other types of gynecologic cancers.
Read More: 10 Important Health Screening Tests for Women in 20s and 30s
4. Transvaginal Ultrasound (TVUS)
Transvaginal Ultrasound (TVUS) is an imaging test that uses high-energy beams to produce images of the organs they target. This technique visualizes the shape, size, and appearance of the ovaries and uterus, helping the physician with ovarian cancer diagnosis.
It is a quick and reliable method for determining the presence of cysts in the ovaries. It also monitors the efficiency of treatment methods and the prognosis of the disease.
Transvaginal ultrasound has low efficacy in determining the presence of ovarian cancer at early stages. Similar to pelvic exams, these ultrasounds cannot differentiate malignant cancer from a non-cancerous mass.
5. Needle Biopsy
In the quest to find better means of ovarian cancer diagnosis, needle biopsy has emerged as a promising method.
This technique is used to collect tissue samples from the different parts of the ovary. A physician then examines these samples for the presence of tumors and cysts.
Needle biopsy is highly sensitive and accurate for determining the presence of tumors in ovaries. It is quick and non-invasive, resulting in its popularity over traditional surgical procedures for ovarian cancer diagnosis. However, in the hands of a novice, there is a slight chance of hitting and rupturing the cysts.

6. Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is a surgical procedure in which the internal organs of the abdomen and pelvis are visualized. It involves a small incision in the abdominal region through which a camera is inserted to examine the ovaries and surrounding organs.
Laparoscopy can also be used to take tissue samples from ovaries. Laparoscopy has little pre and post-operative preparation, slight blood loss, and is less invasive than open surgery.
Read More: 70+ Best Foods for Breast Cancer Prevention
What Happens After Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis?
Receiving an ovarian cancer diagnosis can be quite overwhelming, and you may feel shocked and upset. But remember, beginning the treatment at the right time often guarantees the best results.
A few steps to take when you get your diagnosis are:
- Talk to your family and friends and rally support around you.
- Before moving forward, get a second opinion on your diagnosis.
- Talk to your doctor and ask for a referral to a gynecologic oncologist.
- Discuss different treatment options with your oncologist.
- Gather as much information as you can about ovarian cancer and remain involved in all decisions.
- Don’t hesitate to seek professional help for your emotional wellness and mental health.
- Before initiating any treatment methods, remember to learn a few basics about each procedure. Some treatment options include chemotherapy, radiology, laparotomy, ovariectomy, etc.
The Bottomline
Regardless of the time of diagnosis, ovarian cancer is scary and overwhelming. But always keep an eye on its symptoms so you can identify and seek medical attention on time.
Ovarian cancer diagnosis includes blood tests like CA-125 and HE4 tests, traditional screening procedures like pelvic examination and imaging test, biopsies, and surgical interventions to gather samples and examine the affected ovary.
Remember, the path to a successful treatment strategy is early detection of ovarian cancer. So prioritize your reproductive health, schedule regular check-ups, and discuss changes in your body with your healthcare provider.
References:
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12184039/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7763876/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4102732/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21863264/








