Hey there! This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate, I earn a teensy commission from qualifying purchases when you buy through these links (at no additional cost to you). For more info, please check the full disclaimer.
Uterine fibroids are benign growths affecting millions of women, particularly during reproductive age. While many women experience no symptoms of uterine fibroids, others have to cope with painful consequences.
Either way, recognizing the signs of uterine fibroids is crucial for early detection, accurate diagnosis, and effective treatment.
In this blog, we will shed light on the causes and symptoms of uterine fibroids and how they can impact the overall health status. You’ll also learn about the diagnostic methods and treatment options that can help manage the disease to improve the quality of life.
What are Uterine fibroids?
Uterine fibroids or leiomyomas are the non-cancerous growth of the uterus. They usually comprise of uterine muscles and connective tissues and are not associated with uterine cancer.
They grow in different areas of the uterus and may range from barely detectable globules to large masses. Normally, uterine fibroids can range from 1mm to 20cm in diameter. Many fibroids remain undetected and pose no health risk, while others grow to a noticeable size and can cause harmful symptoms.
According to the Office on Women’s Health, 20%-80% of women develop symptoms of uterine fibroids before the age of fifty.
What are the Main Causes of Uterine Fibroids?
Researches and studies are yet to pinpoint a specific cause of uterine fibroids in women. However, many different reasons can enhance the probability of fibroids in women.
Some of the common causes are discussed below:
- The occurrence of uterine fibroids has a genetic basis and tends to run in families
- Women between 30 and 40 years of age
- African Americans are at greater risk than whites and Hispanics
- Hormonal fluctuations such as high levels of estrogen and progesterone also increase the likelihood of uterine fibroids
- Dietary habits like consuming more red meat and low vegetables and fruits intake
Besides, the presence of the following risk factors may also contribute to the symptoms of uterine fibroids:
- Obesity
- Early start of periods
- Late menopause
- Use of contraceptive methods
- Not having children
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Alcoholism
How Do You Detect Early Uterine Fibroids?
Detection of uterine fibroids is an essential step towards understanding the cause and symptoms of this condition.
Let’s delve into the various physical and diagnostic tools to detect the presence of uterine fibroids:
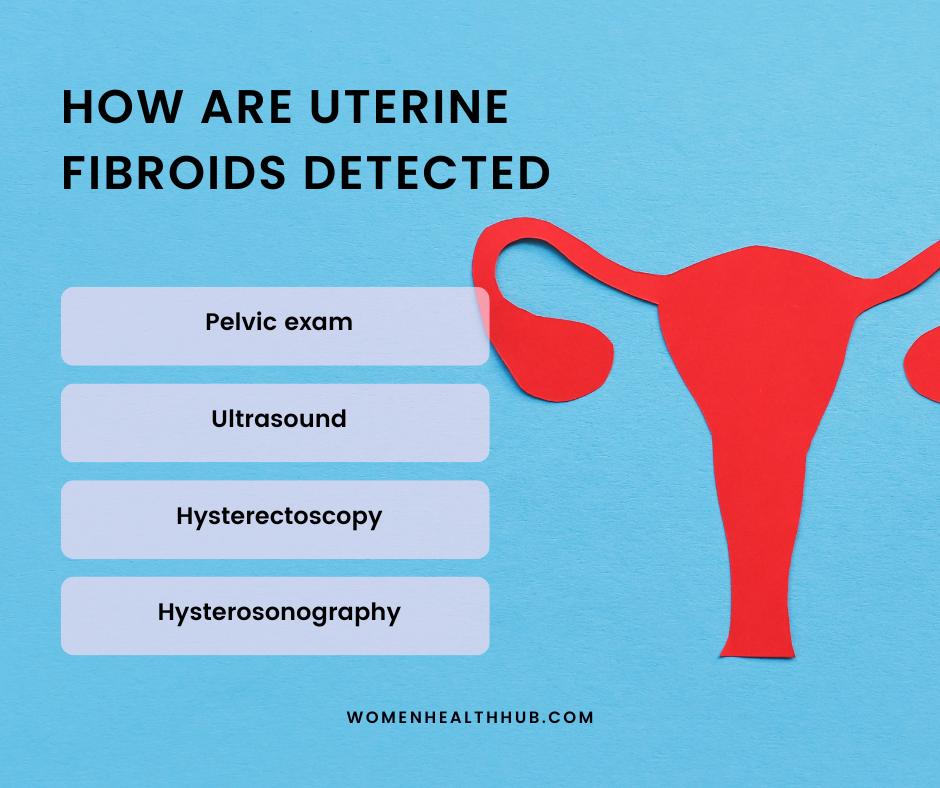
- Pelvic Exam
In a pelvic exam, the gynecologist enters two gloved fingers into the vaginal opening to examine the size and shape of the reproductive organs. Imaging tests are recommended if the physician detects any symptoms of uterine fibroids.
- Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses high-energy X-rays to create a virtual image of the internal organs. The radiologist then examines these organs to determine the presence or growth of any anomaly.
- Hysterosonography
Hysterosonography is used if unspecific signs of uterine fibroids are observed in a patient. In this test, a contrast material is injected into a uterus, and an X-ray is taken. The use of fluorescent dye provides a better visual of the uterus and fallopian tube.
- Hysteroscopy
In hysteroscopy, a thin scope with a light and a camera penetrates the vagina and cervix. The location, size, and number of fibroids in the internal organs can be observed without an imaging test.
Read More: How to Prepare for a Hysterectomy
What are the Common Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids?
50% of women have no apparent symptoms of uterine fibroids, called asymptomatic fibroids. In these cases, the doctors tend to follow the ‘if it ain’t broken, don’t fix it’ rule.
Sometimes asymptomatic fibroids might become painful, so patients are asked to have regular check-ups and monitor the onset of uterine fibroids signs. This helps in getting adequate medical attention at the right time.
A few symptoms of uterine fibroids to keep an eye on are mentioned below.
1. Menstrual Irregularities
Heavy mensural bleeding is one of the tell-tale symptoms of uterine fibroids, observed in about 30% of women. The uterine fibroids push against the uterine lining, damaging the venous drainage system and causing heavy bleeding.
In addition, it may lead to prolonged periods lasting more than one week.
Fibroids are also associated with increased prostaglandin production. Higher levels of prostaglandin trigger severe pain and cramps, common in uterine fibroids.
Read More: Foods to Relieve Period Cramps
2. Pelvic Pain
Pelvic pain is reported by 50% of the patients and is one of the significant signs of uterine fibroid.
The intensity of pelvic pain depends on the size and location of the fibroid. As the uterine fibroid increases in size, the pain may change from dull aches to constant, sharp pain.
The exact cause of pain in the pelvis is unknown, but it can be due to the extra weight of the fibroid on the pelvic joints. The uterine fibroids also push against the surrounding tissues and organs in the pelvic area, which leads to painful sensations.
3. Frequent Urination
Women with fibroids may feel the urge to urinate every short period of time, as frequent urination is another one of the common symptoms of uterine fibroids.
As the uterine fibroids grow, they continue to expand the size of the uterus until it ultimately presses against the urinary bladder. The pressure on the bladder makes you feel like you have to go to the loo every so often.
According to a study, 56% of women are disturbed by the urge to urinate frequently. If the urge is not satisfied frequently, it can also lead to loss of bladder control or urinary inconsistency, particularly in older women.
Read More: Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
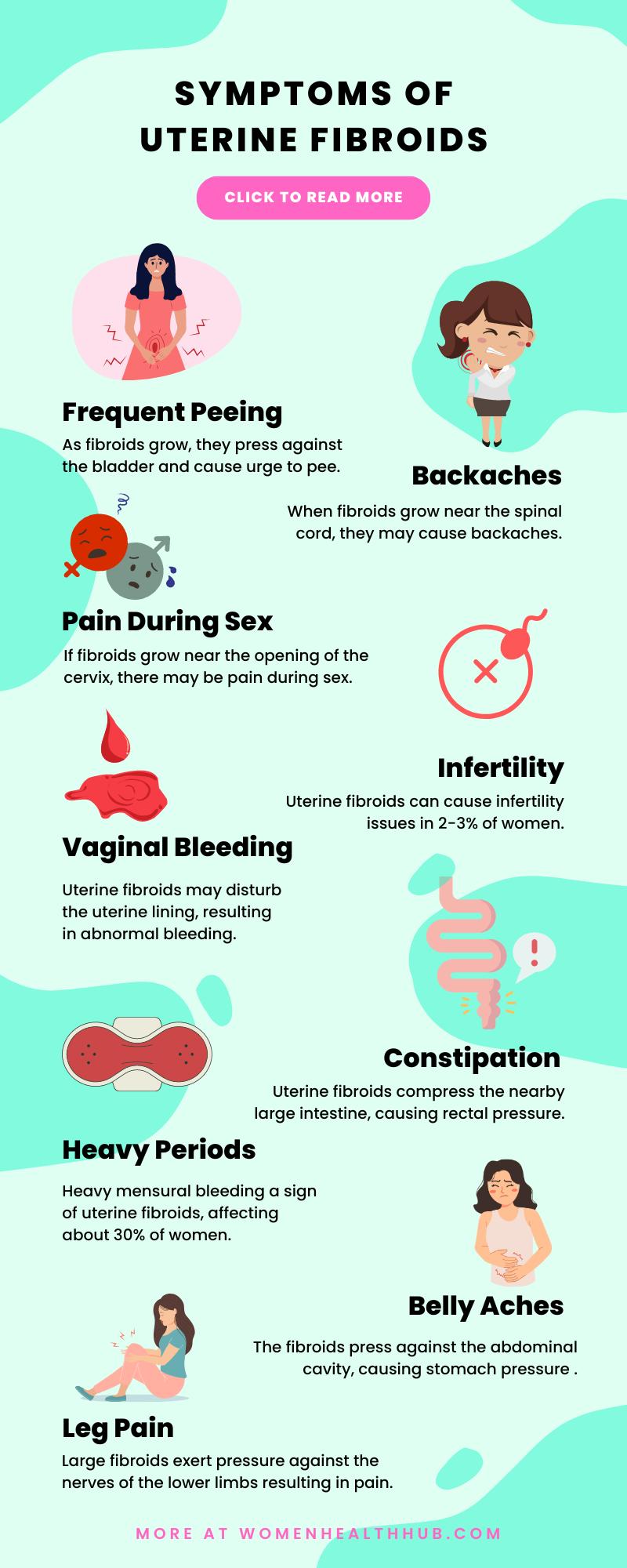
4. Constipation
Constipation is one of the overlooked symptoms of uterine fibroids, and it can significantly impact the gastrointestinal health of women. The effect of fibroids on intestinal functions depends on their number, size, and location in the uterus.
Uterine fibroids compress the nearby large intestine, causing rectal pressure. This pressure makes it difficult to pass the stool, leading to constipation. These women experience straining during bowel movements, infrequent bowel habits, hard stools, and a feeling of incomplete evacuation.
Constipation is also attributed to other physical signs of uterine fibroids like stomachache, bloating, and a sense of heaviness.
5. Abdominal Pain
Many women describe abdominal pain as one of the symptoms of uterine fibroids. The fibroids press against the abdominal cavity, causing pressure on the lower stomach. Abdominal pain may worsen when you exercise, move too quickly, or bend over.
6. Backaches
Most women have reported backache as one of the prevailing symptoms of uterine fibroid. Sometimes uterine fibroids grow at the back of the uterus, near the spinal cord.
As these fibroids grow in size, they protrude into the surrounding network of nerves and muscles. The pressure and displacement caused by fibroids lead to muscle tension, inflammation, and nerve irritation, which is perceived as backache.
Chronic back pain is a constant nuisance that disrupts the daily activities of the patients by limiting mobility and decreasing the quality of life.
Read More: Yoga Poses for Back Pain Relief
7. Leg Pain
One of the most common symptoms of uterine fibroids that grow outside the uterus is pain in the lower extremities. Large fibroids exert pressure against the nerves of the lower limbs resulting in pain.
These fibroids can also irritate the sciatic nerve in the leg, which causes pain at the back of the legs, referred to as sciatica pain.
The large fibroids squeeze the blood vessels, blocking the blood supply to lower limbs which causes the legs to become swollen, causing cramps.
8. Painful Sex
The symptoms of uterine fibroids are related to their size and location. The fibroids that grow near the opening of the cervix can make penetration painful as they are vulnerable to pressure.
Hormonal imbalance, an underlying cause of uterine fibrosis, causes vaginal dryness increasing friction and making sexual intercourse painful.
Many women have reported mild to severe pain in the lower abdomen during sex that may last for hours after intercourse.
Read More: Sex Positions for Increased Pleasure
9. Vaginal Bleeding
Vaginal bleeding is the abnormal discharge of blood or spotting between periods. The presence of uterine fibroids alters the hormonal balance in the body, resulting in irregular bleeding.

The location of the uterine fibroid also plays a crucial role in the onset of many symptoms. If the tumor is located inside the uterus, it can disturb the uterine lining, causing abnormal bleeding even in the absence of menstruation.
10. Vaginal Discharge
Vaginal discharge refers to the clear fluid usually secreted by the vagina. However, if there are changes in the quantity and color of the discharge, it may be one of the symptoms of uterine fibroids.
Heavy vaginal discharge is due to hormonal fluctuations and changes in uterine functioning caused by fibroids. This discharge is usually clear or white, but pink color has been reported due to the presence of blood.
11. Reproductive Issues
Uterine fibroids can cause infertility issues in 2-3% of women. Depending on the size, fibroids block the fallopian tube inhibiting the transport of egg cells. Some fibroids grow in the middle of the uterus, making it impossible for the embryo to implant in the uterine lining.
Women with uterine fibroids have difficulty getting pregnant and having a live birth. The risk of preterm labor, miscarriage at stages of pregnancy, and abnormal fetal presentation are also higher in the presence of uterine fibroids.
Read More: First Trimester of Pregnancy Guide
How are Uterine Fibroids Treated
Many fibroids are not treated as they don’t pose any health risks. In the absence of symptoms of uterine fibroids, the physicians recommend regular pelvic and imaging tests.
However, most women require medical attention as the condition may cause severe pain. In these cases, some treatment options may include:
- Medication
Painkillers are usually recommended to women with severe cramps to subside the pain.
Birth control pills may help reduce the severity of period pain and heavy bleeding during menstruation.
Drugs called Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) agonists are also recommended to women before surgical removal of fibroids. These drugs reduce the size of fibroids so they are easily removed without damaging the surrounding organs.
- Surgery
Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus that also eliminates the growth of fibroids. It is used for large fibroids or severe symptoms of uterine fibroids.
Myomectomy is the removal of fibroids without damaging the uterus. It has different types depending on the size and location of fibroids.
In Uterine fibroid embolization, a catheter is used to block the artery supplying blood to fibroids. The lack of blood supply decreases the size and elevates the symptoms of uterine fibroids.
The Bottomline
Understanding the symptoms of uterine fibroids is crucial for the early detection, diagnosis, and management of this condition. These symptoms can vary in severity and often significantly impact the physical health of the patients.
From heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding to pelvic pain, urinary retention, backache, leg pain, painful sex, and abnormal vaginal bleeding, each symptom highlights the complex nature of uterine fibroids.
By being aware of the causal factors, seeking timely medical attention, and exploring different treatment options, the symptoms of uterine fibroids can be managed effectively.
Remember, you don’t have to face these symptoms alone – reach out to healthcare professionals who can provide guidance, support, and personalized care.
References:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9580818/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34741454/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29054502/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29076451/